Questions
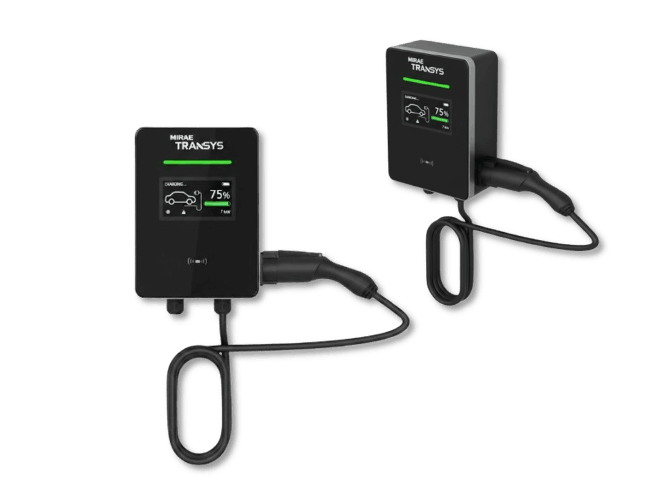
Slow Charging (AC): Uses AC power, which is converted to DC by the on-board charger (OBC). The speed is slow (typically 3–7 kW).
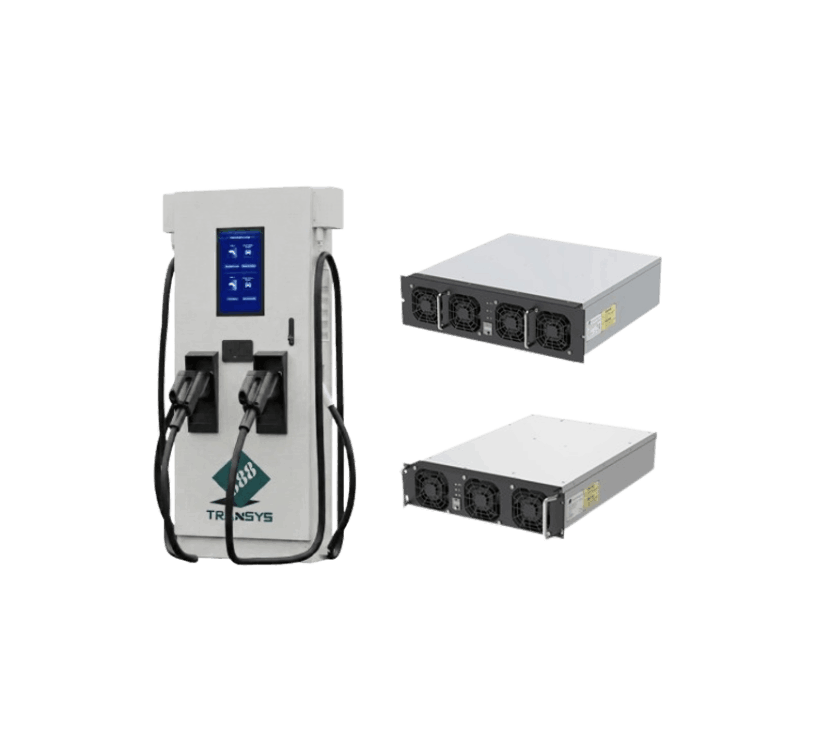
Fast Charging (DC): The charger converts AC to high-power DC and supplies it directly to the battery. It is much faster (typically 50 kW or more).
Korea's Standard: Type 1 (J1772) for slow AC charging and CCS 1 (Combined Charging System 1) for fast DC charging.
Other Standards: International standards include Type 2 and CHAdeMO.
Slow AC Chargers: Generally use AC 220V with 3–7 kW output.
Fast DC Chargers: Use high-voltage/high-current DC, providing various outputs like 50 kW, 100 kW, or 300 kW and higher.
Overcurrent, overvoltage, overheating, or operation above the designed rating.
To eliminate ground loops, protect the system from common-mode noise and surges, and ensure stable operation in interference-sensitive systems.